Kmer Frequency (k=3)
K-mer frequency (with k=3) analyzes trinucleotide patterns within lncRNAs, revealing unique sequence characteristics that differentiate them from other RNA types. This feature aids in understanding lncRNA structure, function, and disease associations by identifying distinct trinucleotide motifs that influence cellular processes and disease mechanisms.
Levenshtein Distance
Levenshtein distance measures sequence dissimilarity by counting the minimal edits needed to transform one sequence into another. In lncRNAs, it helps quantify sequence variation, providing a critical feature for predicting lncRNA functionality and disease associations by capturing subtle sequence differences.
LncRNA Target Association
LncRNA-target associations with proteins, miRNAs, mRNAs, etc., are crucial for understanding lncRNA roles in regulatory mechanisms and disease pathways. This feature enriches models by linking lncRNAs to their functional relevance and potential disease implications, aiding in accurate disease association predictions.
Gaussian Interaction Profile for lncRNAs
The Gaussian Interaction Profile (GIP) represents the interaction strength between lncRNAs and their targets, derived from an lncRNA-disease association matrix. GIP features enhance predictive models by capturing complex lncRNA-target relationships, improving the inference of lncRNA-disease associations.
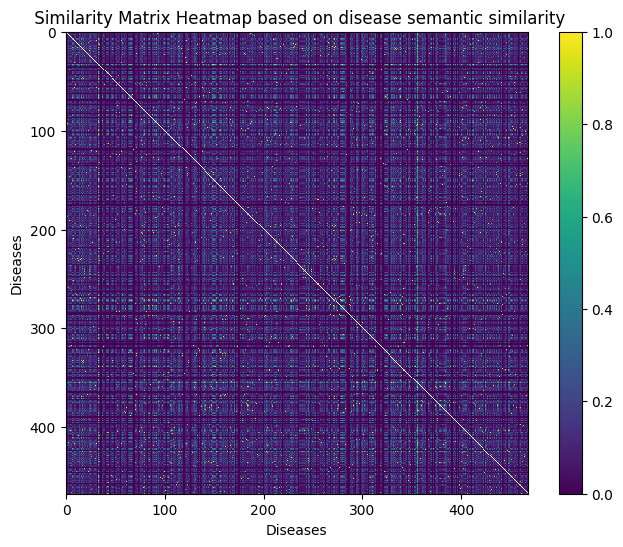
Disease Semantic Similarity
Disease semantic similarity, computed using the DOSE package in R, quantifies the relationships between diseases based on their annotations. Incorporating this feature in lncRNA-disease models allows for a nuanced understanding of disease associations, enhancing prediction accuracy by considering disease proximity and shared biological pathways.
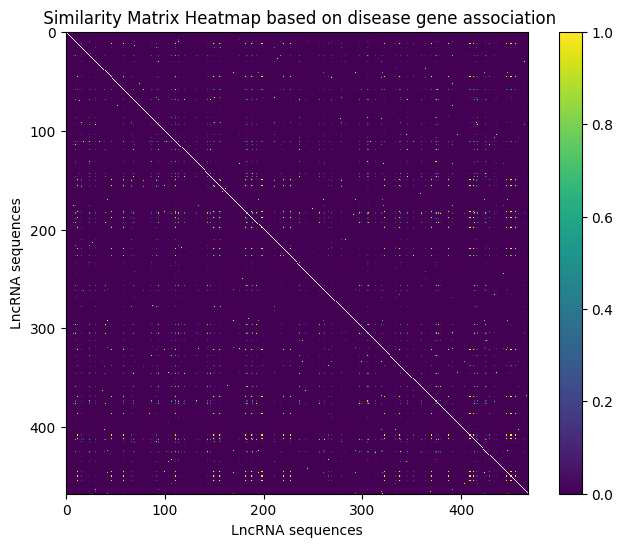
Disease Gene Association
Disease gene associations provide insights into the genetic basis of diseases, enhancing lncRNA-disease association matrices. This feature captures lncRNA interactions with disease-associated genes, aiding in identifying genetic factors linked to diseases and improving the predictive capacity of disease association models.
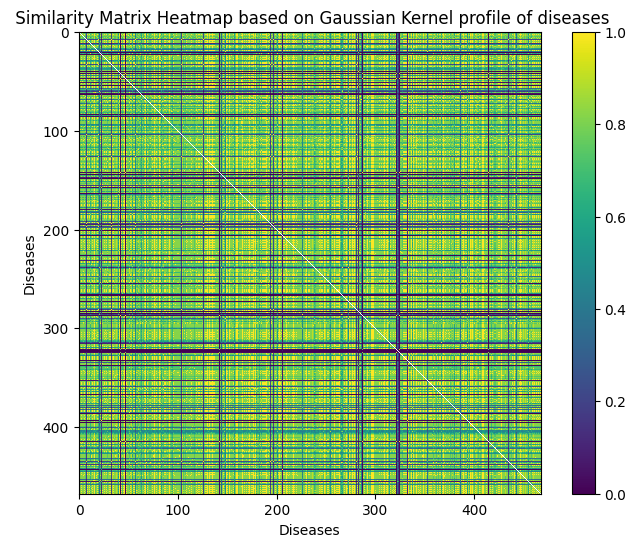
Gaussian Interaction Profile for diseases
The Gaussian Interaction Profile (GIP) for diseases, derived from an lncRNA-disease association matrix, encodes disease relationships in a continuous space. By transforming association scores into Gaussian-distributed values, GIP features capture underlying patterns, enabling machine learning models to make accurate lncRNA-disease predictions.